- The Pound Sterling faces slight selling pressure as the BoE is widely expected to cut interest rates in May.
- BoE’s Greene expects that Trump’s tariff policy will be disinflationary for the UK economy.
- Washington says that China should be the one to initiate bilateral trade talks.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) edges lower against its major peers on Tuesday in the European session. The British currency ticks down as traders become increasingly confident that the Bank of England (BoE) will reduce interest rates in the May policy meeting. The reasons behind these accelerating BoE’s dovish bets are easing United Kingdom (UK) inflation expectations and heightened global economic tensions.
Officials from central banks across the globe have signaled that the impact of protectionist policies imposed by Washington will be net disinflationary for their economies, assuming that domestic companies – and particularly Chinese companies – will be forced to sell their products in other markets at lower rates in the face of higher tariffs from the US.
On Friday, BoE policymaker Megan Greene also indicated that the potential trade war will be “net disinflationary” for the economy in a discussion with the Atlantic Council think tank. Greene also expressed concerns over “weak productivity” and “risks to the labor market” due to an increase in employers’ contributions to social security schemes.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling retraces against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling corrects marginally to near 1.3400 against the US Dollar (USD) during European trading hours on Tuesday from its fresh three-year high of 1.3445 posted earlier in the day. The GBP/USD pair retraces as the US Dollar steadies, with investors awaiting a slew of United States (US) economic data releases.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades inside Monday’s range at around 99.20.
- This week, investors will pay close attention to labor market-related, ISM Purchasing Manager’s Index (PMI), Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index (PCE), and Q1 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data to get cues about the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook.
- The major highlight of the week is expected to be the ISM Manufacturing PMI data, which will indicate the impact of the tariff policy announced by US President Donald Trump on the input cost and how much factory owners are willing to pass on to consumers.
- Signs of increasing selling prices by factory owners would accelerate consumer inflation expectations. Such a scenario would be a limiting factor for the Federal Reserve (Fed) in reducing interest rates.
- In Tuesday’s session, investors will focus on the US JOLTS Job Openings data for March, which will be published at 14:00 GMT. The Job Openings data is expected to show that employers posted 7.5 million jobs, marginally lower than the 7.56 million seen in February.
- Meanwhile, higher uncertainty over trade relations between the US and China will keep the Greenback on the back foot. A fresh boost to US-China trade uncertainty has come from US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, who has put the responsibility for any progress in bilateral trade on Beijing. “I believe that it’s up to China to de-escalate, because they sell five times more to us than we sell to them,” Bessent said in an interview on CNBC’s Squawk Box on Monday.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling stays above all short-to-long-term EMAs
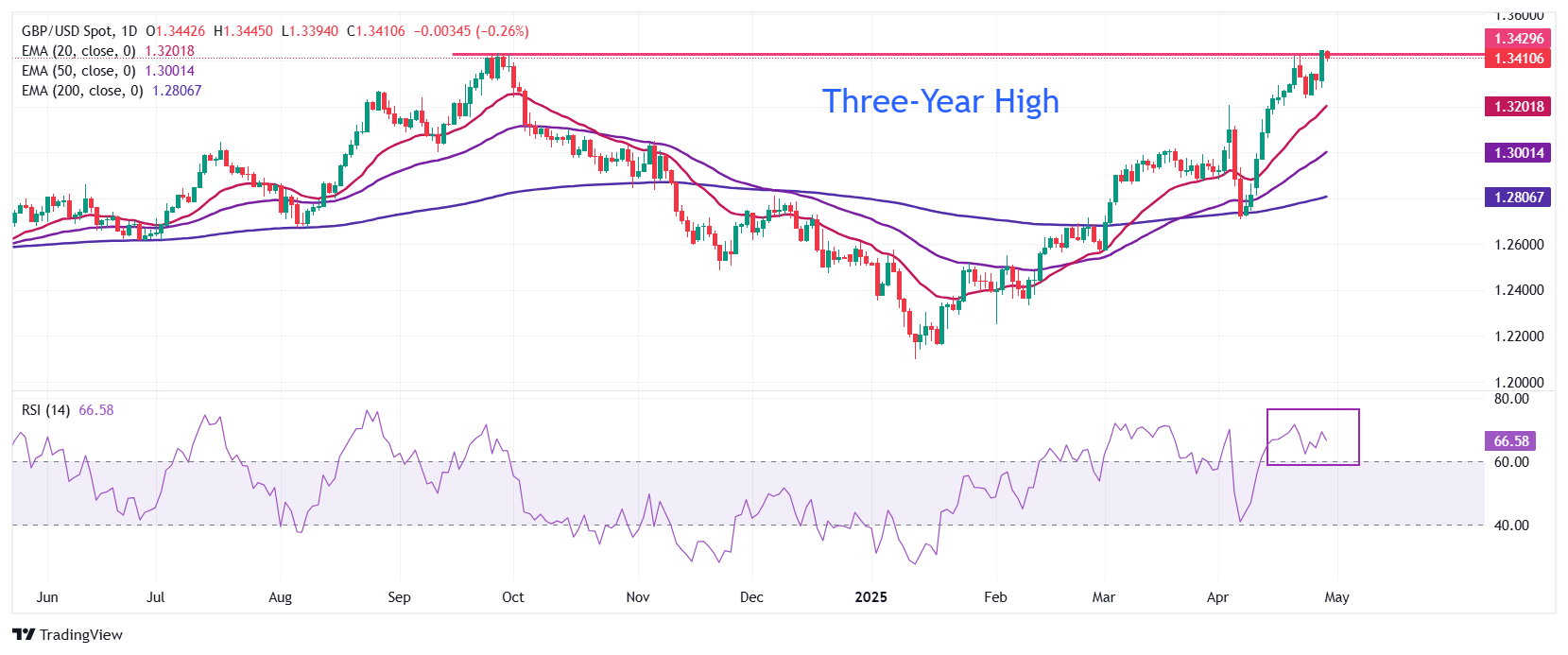
The Pound Sterling retraces slightly to near 1.3400 against the US Dollar from the three-year high of 1.3445. The overall outlook of the pair remains bullish as all short-to-long Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) are sloping higher.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) rebounds after cooling down to 60.00, indicating a resurgence in the upside trend.
On the upside, the round level of 1.3600 will be a key hurdle for the pair. Looking down, the April 3 high around 1.3200 will act as a major support area.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data.
Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates.
When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP.
A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period.
If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

