- USD/CAD trades sideways around 1.3730 as investors await the Canadian labor market data for July.
- The Canadian Unemployment Rate is seen higher at 7%.
- Accelerating Fed’s interest rate cut bets have weighed on the US Dollar.
The USD/CAD pair trades in a tight range around 1.3730 during the European trading session on Friday. The Loonie pair consolidates as investors await the Canadian labor market data for July, which will be published at 12:30 GMT.
Investors will closely monitor the employment data as it will influence market expectations for the Bank of Canada’s (BoC) monetary policy outlook.
Economists expect the Canadian economy to have created 13.5K fresh jobs, lower than 83.1K in May. The Unemployment Rate is seen at 7%, higher from the prior release of 6.9%.
During European trading hours, the US Dollar (USD) struggles to gain ground, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) edging marginally up, but stays close to more-than-a-week low around 98.00.
The US Dollar faces selling pressure as the Federal Reserve (Fed) is almost certain to cut interest rates in the September policy meeting, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
Meanwhile, a report from Bloomberg has shown that Fed Governor Chrisopher Waller could be chosen as Chairman Jerome Powell’s successor.
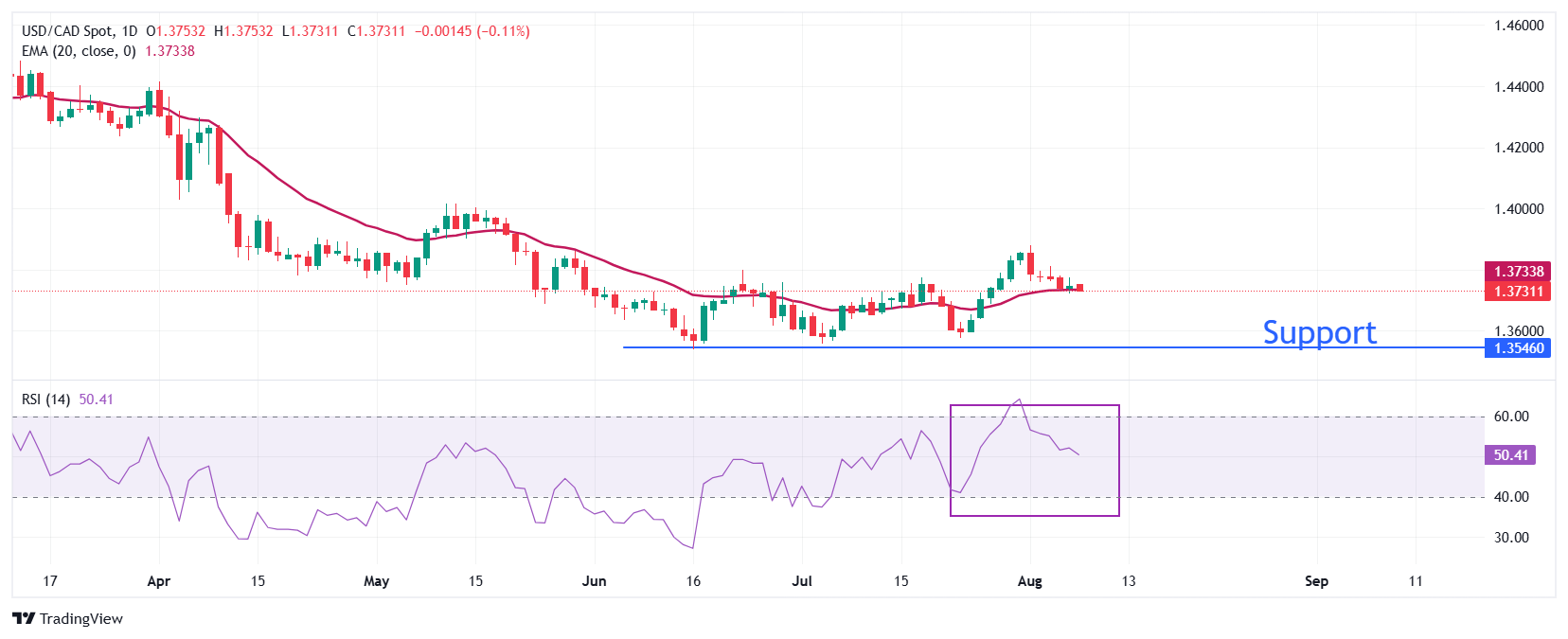
USD/CAD trades cautiously near the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.3730. The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) oscillates around 50.00, indicating a sideways trend.
Going forward, an upside move by the pair above the August 1 high of 1.3880 would open the door towards the May 15 high of 1.4000, followed by the April 9 low of 1.4075.
On the contrary, the asset could slide towards the psychological level of 1.3500 and the September 25 low of 1.3420 if it breaks below the June 16 low of 1.3540.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

