- EUR/USD down 0.30%, trading at 1.1605 after touching daily high of 1.1675.
- US Dollar bought ahead of US July CPI release; hot print could dampen Fed rate cut bets.
- Italy’s July inflation steady at 1.7% YoY, matching ECB target and June reading.
- Trump–Putin talks may yield Ukraine ceasefire progress, potentially easing EU energy costs.
The EUR/USD edges lower on Monday, down 0.26% as the Greenback is bought by traders ahead of another inflation report in the United States (US) coming Tuesday. This, along with Italy’s revelation that prices reached the European Central Bank’s (ECB) target, justifies the need to hold rates even at the next meeting. The pair trades at 1.1615 after hitting a daily high of 1.1675.
The shared currency halted its advance, even though talks between US President Donald Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin are expected to show progress on a possible ceasefire in Ukraine. A favorable resolution could unleash the Euro as most European Union (EU) countries are net importers of energy, and a ceasefire or peace plan could push prices lower due to de-escalation of the conflict.
Traders are also eyeing the release of the July Consumer Price Index (CPI) figures in the US. If prices jump, exceeding forecasts, market players could begin to price out the chances of a 25-basis-point rate cut by the Federal Reserve (Fed).
Across the pond, Italy reported that inflation rose by 1.7% YoY in July, which was as expected and unchanged from June’s data.
Ahead, the EU’s docket will feature the EU and Germany ZEW Survey for August, French inflation, and growth data for the bloc. In the US, the economic schedule is expected to announce inflation on the consumer and the producer fronts, Fed speeches, jobless claims, Industrial Production data, Retail Sales, and the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment for August.
Euro PRICE This week
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies this week. Euro was the strongest against the British Pound.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.01% | -0.00% | -0.02% | -0.10% | -0.03% | |
| EUR | -0.03% | 0.00% | -0.02% | -0.01% | -0.02% | -0.12% | -0.03% | |
| GBP | -0.03% | -0.01% | 0.08% | -0.01% | -0.03% | -0.10% | -0.04% | |
| JPY | -0.01% | 0.02% | -0.08% | 0.00% | -0.05% | -0.11% | 0.06% | |
| CAD | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.01% | -0.00% | 0.02% | -0.11% | -0.02% | |
| AUD | 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.03% | 0.05% | -0.02% | -0.09% | -0.02% | |
| NZD | 0.10% | 0.12% | 0.10% | 0.11% | 0.11% | 0.09% | -0.02% | |
| CHF | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.04% | -0.06% | 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.02% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
Daily digest market movers: Euro falls on traders booking profits, awaiting inflation data
- The EUR/USD dives as investors brace for the release of July’s CPI data. Estimates suggest that headline prices are expected to accelerate by 2.8% YoY, up from 2.7% in June. Likewise, the core CPI is projected to hit the 3% threshold for the first time since February.
- If indeed US inflation rises, expect further EUR/USD downside due to increased chances that the Fed might hold rates unchanged at the September meeting.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the buck’s value against a basket of its peers, is up 0.26% at 98.52.
- The Eurozone economic schedule will be light as investors await the release of the EU and Germany’s ZEW Surveys, inflation in Germany, Eurozone employment and growth figures.
- The latest economic data released in the US spurred investor speculation that the Fed might resume its easing cycle at the upcoming September meeting. Odds for a quarter of a percentage cut are at 85%, according to the Prime Market Terminal.
- On the European Central Bank (ECB) front, the easing cycle seems to be on pause for the September meeting, with 91% odds for the ECB to keep rates unchanged and a slim 9% chance of a 25bps rate cut.
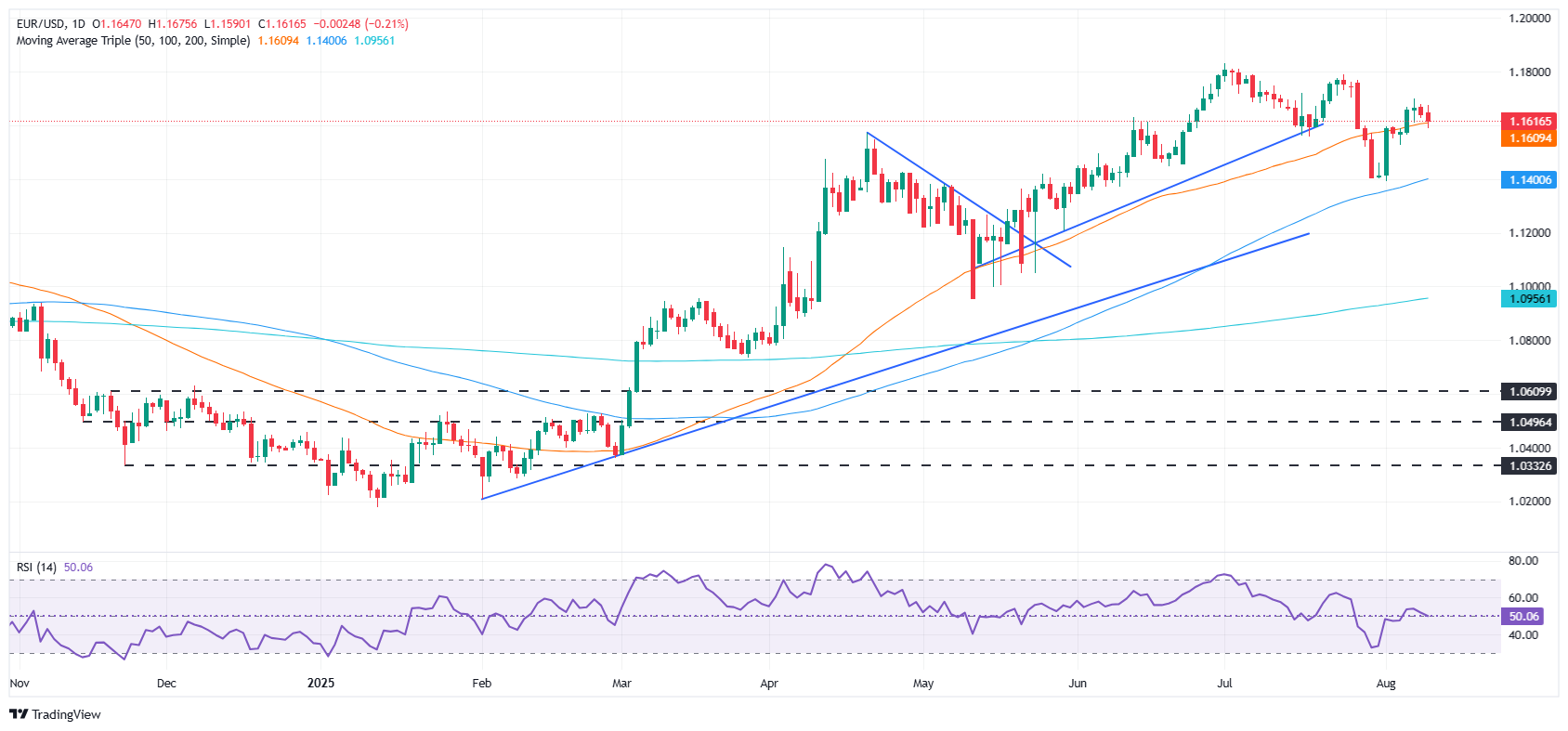
Technical outlook: EUR/USD tumbles to 1.1600 as traders eye break of key support level
The EUR/USD advance has halted, posting back-to-back bearish candles, though the pair remains above the 1.1600 figure. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) shows that buyers seem to be losing momentum as the index falls below its 50 neutral level, turning bearish.
With that said, sellers need to push the pair below 1.1600 daily. If achieved, the next support would be the August 5 low of 1.1527. A breach of the latter will expose 1.1500. Conversely, if EUR/USD stays above 1.1600, traders would eye 1.1650 ahead of cracking the 1.1700 mark.
ECB FAQs
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region.
The ECB primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa.
The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro.
QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.

