- EUR/USD trades sideways around 1.1370 ahead of the Fed’s monetary policy decision.
- Investors will focus on the Fed’s guidance on the monetary policy outlook.
- Conservative leader Merz was sworn in as German Chancellor in his second attempt.
EUR/USD trades flat near 1.1370 during European trading hours on Wednesday. The major currency pair consolidates as the US Dollar (USD) trades flat ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy announcement at 18:00 GMT. The Euro (EUR) trades firmly against its other peers after Conservative leader Friedrich Merz was sworn in as Chancellor of Germany in a second attempt. Merz failed to secure an absolute majority in the first attempt despite CDU/CSU and Social Democrats collectively having a vote bank of 326. Merz received 310 votes in the first attempt, six fewer than the 316 required to be elected as German Chancellor.
The confirmation of Friedrich Merz as Chancellor has diminished fears of political instability and is expected to boost defense spending measures approved in March. This scenario would strengthen the German economy and favor the Euro and German assets.
However, the upside in the Euro appears to be limited as the European Central Bank (ECB) is set to continue easing the monetary policy in the June meeting. The ECB is almost certain to cut its key interest rates again next month as officials are more focused on absorbing economic shocks in the face of tariffs announced by US President Trump than Eurozone inflation, which is expected to return to the central bank’s target of 2% this year
On the global front, the European Union (EU) Commission is actively considering measures to offset the impact of higher tariffs by the US. On Tuesday, EU Trade Commissioner Maros Sefcovic stated that the continent is exploring countermeasures while Trump has delayed reciprocal tariffs by 90 days. However, Sefcovic clarified that the foremost priority of the EU is trade resolution with the US. A Bloomberg report showed on Tuesday that the EU plans to hit about 100 billion Euros worth of US goods with additional tariffs if trade talks fail to deliver a satisfactory result for the bloc.
On the economic front, EU Retail Sales data for March came in weaker than expected. The Retail Sales data, a key measure of consumer spending, declined by 0.1% on month, while investors expected a flat performance. In February, the consumer spending measure rose by 0.2%, revised lower from 0.3%. Year-on-year Retail Sales grew by 1.5%, slower than estimates of 1.6% and the prior release of 1.9%, revised lower from 2.3%.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD trades flat, investors await US-China trade talks
- EUR/USD wobbles ahead of the Fed’s interest rate decision. According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders have fully priced in that the Fed will leave interest rates steady in the current range of 4.25%-4.50%. Investors will pay close attention to the monetary policy statement and Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference to get fresh cues about how long the central bank will maintain a restrictive monetary policy stance.
- Fed officials have indicated that monetary policy adjustments are not appropriate until they see cracks in the labor market and economic growth, as consumer inflation expectations have de-anchored due to the fallout of new economic policies by United States (US) President Donald Trump.
- April’s Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data showed steady job growth, a limiting factor for the Fed in reducing interest rates. Meanwhile, the US economy contracted by 0.3% in the first quarter of the year, but the reason was the significant surge in imports frontloaded by US business owners to avoid the impact of higher tariffs.
- Contrary to the Fed’s guidance, President Trump has repeatedly urged the central bank, especially Jerome Powell, to lower interest rates. Trump also threatened to discharge Powell from his duties for not reducing borrowing costs despite easing energy prices, food items, etc.
- Ahead of the Fed’s policy, the US Dollar wobbles in a tight range, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) consolidating around 99.55.
- Apart from the Fed policy, the US-China trade talks in Geneva are a major trigger for the US Dollar. US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and Trade Representative Jamieson Greer confirmed on late Tuesday that they will meet their Chinese counterparts for trade discussions. Investors see this as a constructive step towards de-escalation in the Sino-US trade war, which has supported S&P 500 futures.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD wobbles around 1.1350
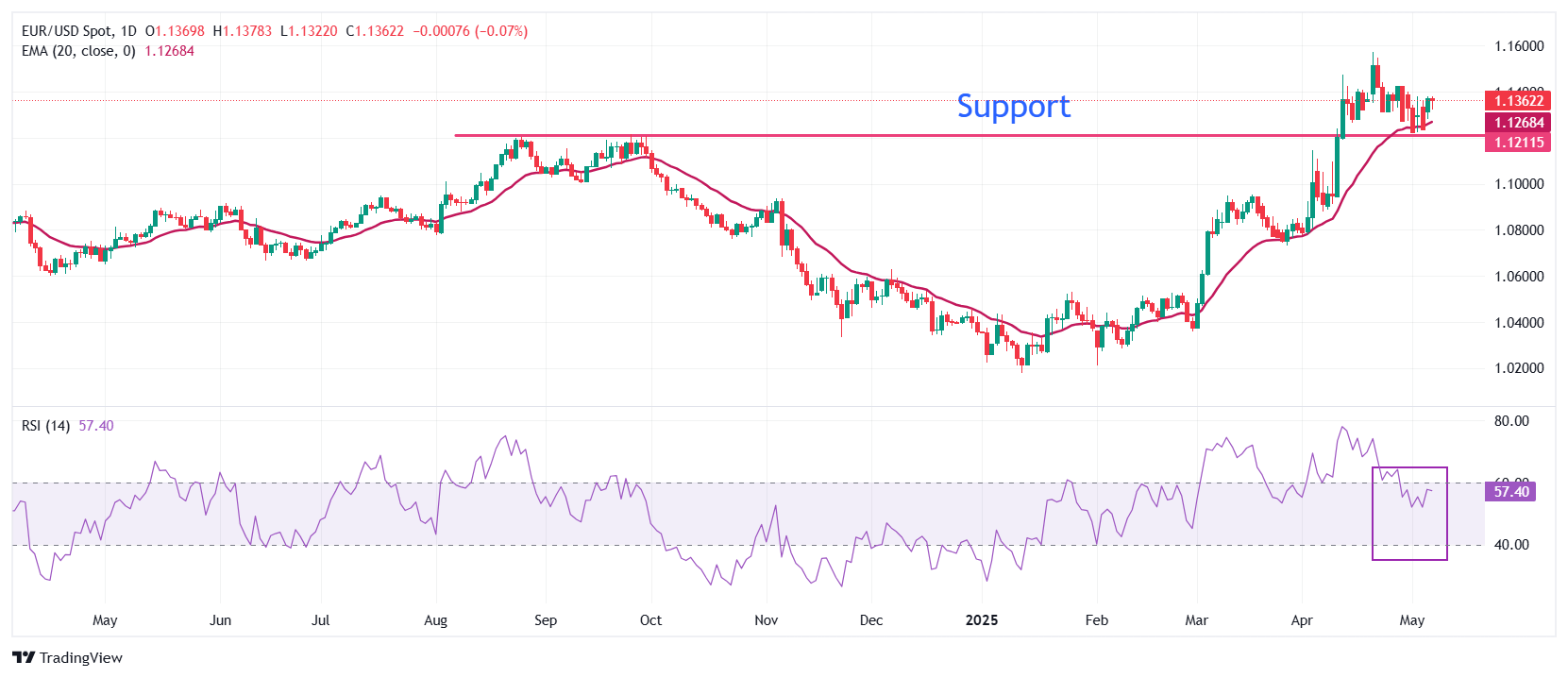
EUR/USD struggles near Tuesday’s high around 1.1370 on Wednesday. However, the outlook of the pair remains bullish as it holds the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.1270.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls inside the 40.00-60.00 range, indicating that the bullish momentum is concluded for now. However, the upside bias still prevails.
Looking up, the psychological level of 1.1500 will be the major resistance for the pair. Conversely, the 25 September high of 1.1214 will be a key support for the Euro bulls.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates.
When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.

