- EUR/USD briefly corrects below 1.1400 as the US Dollar rebounds after Trump pushes back fears of Fed Powell’s removal and intense tariff war with China.
- Trump says that tariffs on China won’t be as high as 145%.
- The Eurozone PMI suggests the economy barely grew in April as the service sector activity contracts.
EUR/USD trades broadly stable on Wednesday after dipping well below 1.1400 earlier in the European trading hours. The major currency pair is off from its over three-year high of 1.1575 as the US Dollar (USD) bounces back. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, has rebounded to near 99.30 from its three-year low of 98.00.
The USD attracts bids after United States (US) President Donald Trump expressed confidence in closing a trade deal with China and backed away fears of sacking Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell. Still, he said, he remained frustrated over the Fed’s decision to keep interest rates on hold for an uncertain period of time.
Financial market participants are seeing this event as an attempt to regain the “safe-haven” status of the US Dollar. Investors had been doubting the credibility of the US Dollar and US assets due to back-and-forth announcements on tariff policies by Donald Trump and his attacks on the autonomous status of the Fed.
On Tuesday, US President Trump stated that discussions with China are going well, adding that he thinks they will reach a deal. Trump didn’t provide clarity over how much he will reduce import duty on China, but clarified that the tariff on Beijing “would not be as high as 145%, but they wouldn’t be zero”.
President Trump pushed back against market expectations that he is aiming to remove Jerome Powell for not lowering interest rates. “The press runs away with things. No, I have no intention of firing him. I would like to see him be a little more active in terms of his idea to lower interest rates,” Trump said.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD expected to face pressure from weak Eurozone PMI data
- The downside move in the EUR/USD pair seen during the early European session is also driven by the Euro’s (EUR) underperformance due to weakness in the domestic business activity. Preliminary Hamburg Commercial Bank (HCOB) Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for April has shown that overall business activity has barely managed to stay in the expanding territory.
- The Composite PMI has come in lower at 50.1 compared to estimates of 50.3 and the March reading of 50.9. A figure below the 50.0 threshold is considered a contraction in private sector activity. A sharp slowdown in the overall PMI data came from an unexpected decline in the service sector activity.
- The Service PMI declined to 49.7, while it was expected to grow at a moderate pace to 50.5 from the prior release of 51.0. Meanwhile, activities in the manufacturing sector continued to contract, but at a slower-than-expected pace. The Manufacturing PMI came in at 48.7, higher than estimates of 47.5 and the previous release of 48.6.
- Commenting on the flash PMI data, Dr. Cyrus de la Rubia, Chief Economist at HCOB, has warned that the weak trend in the service sector could continue as the “new business has seen a faster drop”. However, de la Rubia remained confident that “higher fiscal spending on infrastructure in Germany and defence spending across Europe should eventually benefit not just manufacturing but also the service sector, though with a bit of a lag”.
- Meanwhile, firming expectations that the European Central Bank (ECB) could cut interest rates again in the June policy meeting are also adding to weakness in the shared currency. Traders have become increasingly confident that the ECB could cut interest rates again in June as officials, including President Christine Lagarde, are confident that inflation will return to the central bank’s 2% target soon.
- Christine Lagarde expressed confidence in an interview with CNBC on Tuesday that the “disinflationary path is clearly on its way”, adding that inflation could be seen around 2.1% by the year-end. Lagarde refrained from guiding the monetary policy path. “Either we cut or pause, but we will be data dependent to the extreme,” Lagarde said.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD drops below 1.1400
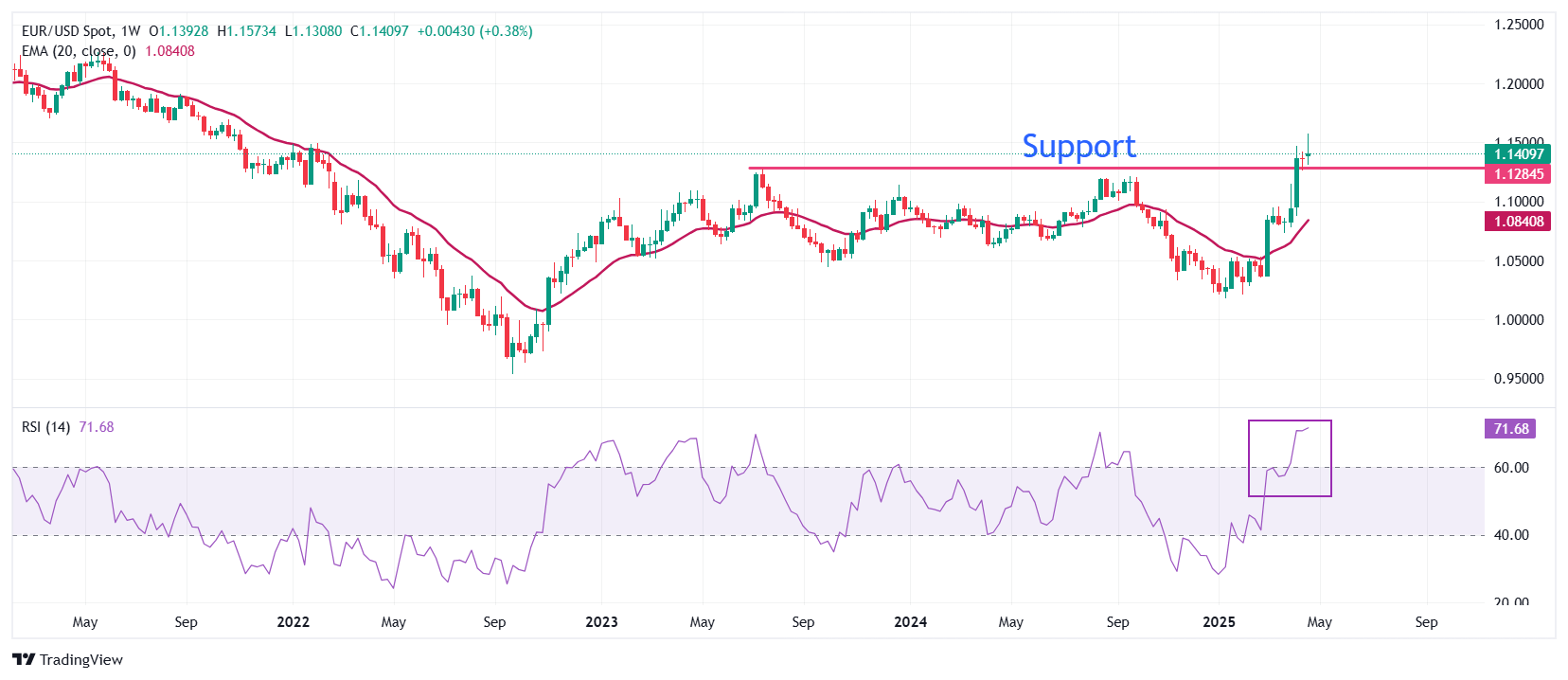
EUR/USD briefly dipped below 1.1400 on Wednesday after facing selling pressure above 1.1500 on Tuesday and recovered afterwards. The major currency pair had shown a strong rally in the last few weeks after a breakout above the September 25 high of 1.1215. Advancing 20-week Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.0840 suggests a strong upside trend.
The 14-week Relative Strength Index (RSI) climbs to overbought levels above 70.00, which indicates a strong bullish momentum but also signals increasing chances of a correction.
Looking up, the round-level figure of 1.1600 will be the major resistance for the pair. Conversely, the July 2023 high of 1.1276 will be a key support for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
BRANDED CONTENT
Finding the right broker for trading EUR/USD is crucial, and we’ve identified the top choices for this major currency pair. Read about their unique features to make an informed decision.

