- The Euro retreats further with the US Dollar rallying as traders’ gaze shifts to the Fed.
- The upbeat US macroeconomic figures offset the impact of a hawkish ECB statement.
- Hopes that the US-EU trade deal is within reach keep EUR downside attempts limited.
The EUR/USD pair is extending losses on Friday with the US Dollar is a tad firmer, supported by positive US macroeconomic data which provide further reasons for the Federal Reserve (Fed) to keep rates ar high levels for a longer time after next week’s meeting, while a poor Business Climate survey from Germany has added weight on the Euro.
The Euro (EUR) is coming into growing bearish pressure, heading into the US session opening. The pair has extended its reversal to 1.1710 at the time of writing, from the 1.1790 high hit on Thursday, following the ECB’s monetary policy decision. The pair, however, remains on track for a 0.8% weekly appreciation, after bouncing from 1.1555 in the previous week.
The ECB boosted the Euro on Thursday as President Christine Lagarde hinted at a longer interest rate pause. Lagarde stuck to her classical “meeting by meeting” approach on interest rates, but she showed optimism about the growth outlook and stated that inflation risks are strongly anchored, casting doubts about further cuts this year.
Eurozone data released on Friday, however, has failed to provide any significant support to the Euro. The US IFO Business Climate Index improved less than expected in July, with German businesses slightly more positive about the current economic situation, but their sentiment about the near-term outlook has remained flat, against hopes of an improvement.
In the US, business activity beat expectations, led by a significant improvement in the services sector, while the weekly Initial Jobless Claims fell against expectations, giving further reasons to the Fed to wait for more clarity about the impact of US tariffs on inflation and economic growth. The US Dollar extended its recovery after the data.
Euro PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies today. Euro was the strongest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.11% | 0.41% | 0.53% | 0.29% | 0.51% | 0.30% | 0.16% | |
| EUR | -0.11% | 0.33% | 0.40% | 0.20% | 0.30% | 0.19% | 0.03% | |
| GBP | -0.41% | -0.33% | 0.08% | -0.15% | -0.02% | -0.12% | -0.30% | |
| JPY | -0.53% | -0.40% | -0.08% | -0.24% | -0.08% | -0.22% | -0.37% | |
| CAD | -0.29% | -0.20% | 0.15% | 0.24% | 0.26% | 0.00% | -0.17% | |
| AUD | -0.51% | -0.30% | 0.02% | 0.08% | -0.26% | -0.12% | -0.24% | |
| NZD | -0.30% | -0.19% | 0.12% | 0.22% | -0.00% | 0.12% | -0.15% | |
| CHF | -0.16% | -0.03% | 0.30% | 0.37% | 0.17% | 0.24% | 0.15% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
Daily digest market movers: Euro remains supported on hopes of a trade deal
- The Euro is on track for a strong performance this week, fuelled by hopes of an imminent trade deal with the US. European Commission sources revealed that the deal includes 15% tariffs with exemptions for some products like automobiles or alcohol, which would avert the 30% levy announced by US President Donald Trump earlier this month.
- On Friday, the German IFO Business Climate Index showed a meager advance, to 88.6 from the previous 88.4, against expectations of an 89.0 reading. The current Situation subindex rose to 86.5 from 86.2, also below the market consensus of 86.7, while the Expectations gauge remained unchanged at 90.7 against market hopes of an improvement to 91.1.
- The pair, however, lost ground on Thursday, as the US flash S&P Global PMI showed that the Service’s activity expanded to a 55.2 level in July, from 52.9 in June, beating expectations of a 53.0 reading. The Manufacturing PMI fell to 49.5 from 52.0 in the previous month and against expectations of an improvement to 52.5. The Composite index rose to 54.6 in July, from 52.9 in June.
- At the same time, data from the US Department of Labour revealed that Initial Jobless Claims declined for the sixth consecutive week to a three-month low of 217K, from the previous week’s 221K, against expectations of an increase to 227K.
- Earlier on Thursday, the ECB left its Deposit Rate unchanged at 2%, as widely expected, and President Christine Lagarde affirmed that economic growth is “in line, if not better than the baseline” and observed that long-term rate expectations remain around the 2% target, hinting at a larger rate pause.
- In the US, Durable Goods Orders are seen contracting at a 10.8% pace after a 16.4% rise in June. Core orders, which exclude transportation, are expected to have slowed down to 0.1% from last month’s 0.5% growth.
EUR/USD shows a growing bearish momentum below 1.1735
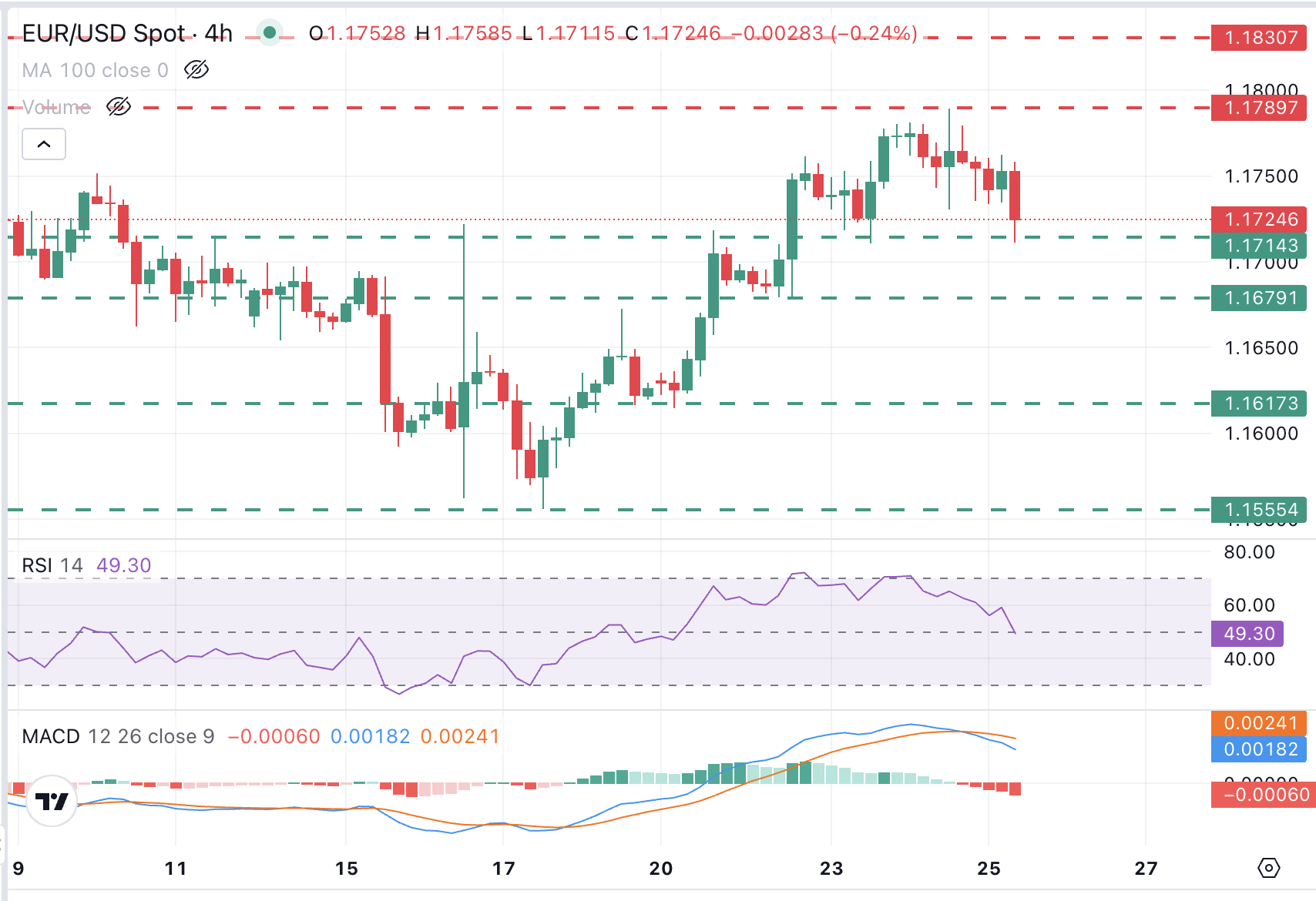
EUR/USD is showing a growing bearish momentum ahead of the US session opening. The pair has broken below Thursday’s lows at 1.1735, leaving bears in control and with technical indicators pointing lower. The MACD has crossed below the signal line in 4-hour charts, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) in the same timeframe is testing the key 50 level.
The pair is now testing support at the 1.1715 area, July 23 low, and the July 16 and 21 highs, ahead of the July 22 low, at 1.1680. On the upside, Thursday’s high, at 1.1790, is likely to challenge bulls ahead of the multi-year high at 1.1830.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.

