- USD/CHF gains traction to around 0.8225 in Wednesday’s early European session.
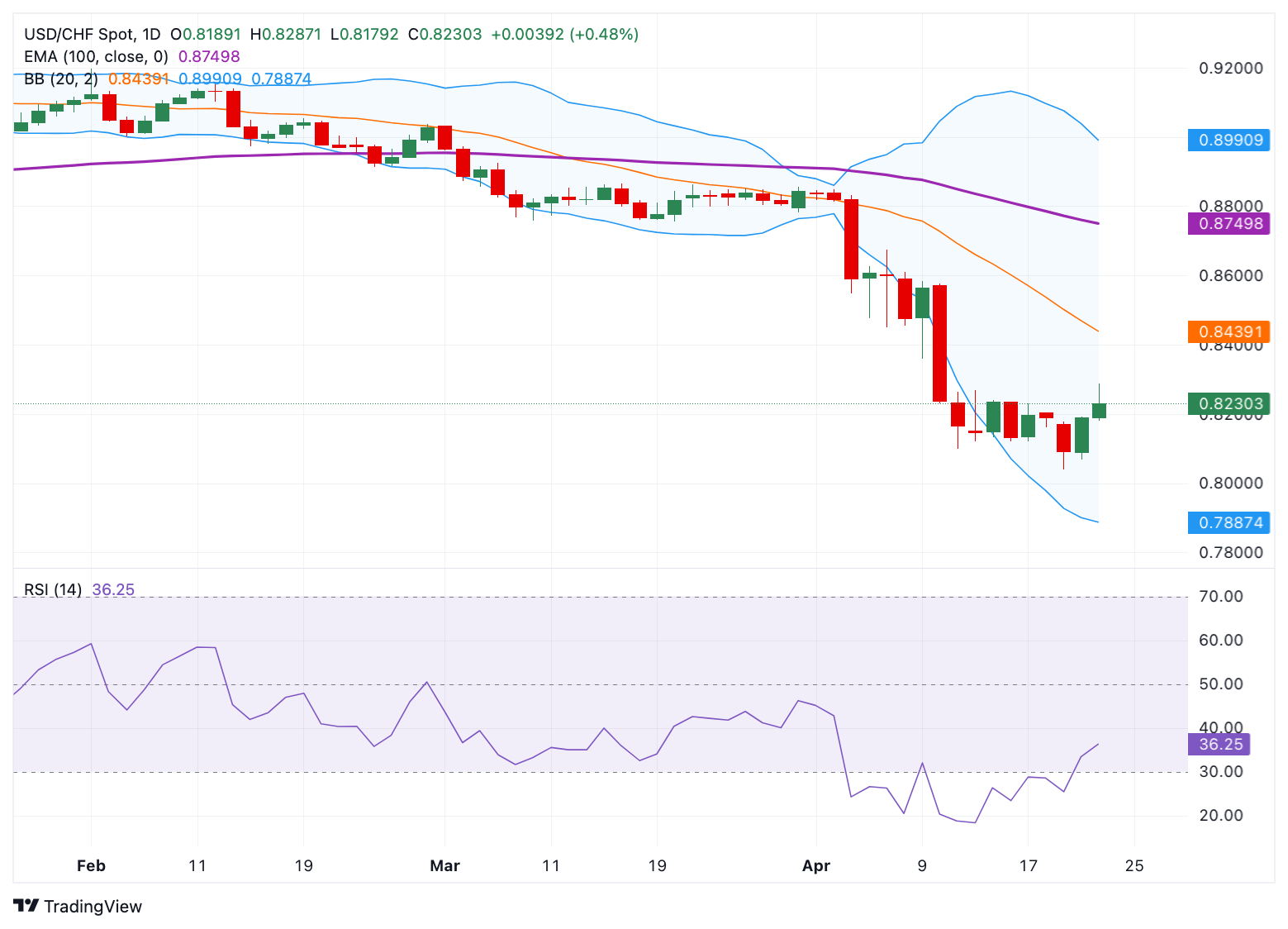
- The negative outlook of the index remains in play below the 100-day EMA with a bearish RSI indicator.
- The first support level to watch is 0.8121; the immediate resistance level is seen at 0.8360.
The USD/CHF pair drifts higher to near 0.8225 during the early European session on Wednesday, bolstered by the renewed US Dollar (USD) demand. Hope for the US-China trade deal provides a boost for investors. Additionally, US President Donald Trump backed away from threats of firing Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell, which provides some support to the Greenback.
According to the daily chart, the bearish sentiment of USD/CHF prevails as the pair is below the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Furthermore, the downward momentum is supported by the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI), which stands below the midline near 36.0, supporting the sellers in the near term.
The initial support level for the pair emerges at 0.8121, the low of April 16. Further south, the additional downside filter to watch is 0.8040, the low of April 21. The key contention level is seen at the 0.8000 psychological level.
On the flip side, the first upside barrier for USD/CHF is located at 0.8360, the low of April 9. Any follow-through buying above this level could pave the way to 0.8609 the high of April 8. A decisive break above the mentioned level could see a rally to 0.8750, the 100-day EMA.
USD/CHF daily chart
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.

