- The US Dollar Index recovers in full and erases the Asian dip seen on Monday.
- The brief euphoria quickly fades on US tariffs delaying on EU goods.
- The US Dollar Index is back to flat at $$.10.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, is turning flat halfway through the European trading session at 99.10. The dip in the Greenback came after the United States (US) President Donald Trump agreed to extend the deadline of the 50% tariffs on the EU to July 9, instead of June 1, when they were supposed to become effective. Overall, a sigh of relief ripples through markets with risk assets emerging as the biggest winners on these developments at the start of the week.
Several traders and analysts are still pointing to persistent issues that remain sticky. The tax bill from President Trump is on its way to be voted on in the Senate, and will add extra pressure on the US debt. With a further ballooning deficit, yields could still rise more, with traders demanding a higher premium for them to buy US debt.
Daily digest market movers: US Public Holiday means low volumes
- Speculative traders remained bearish on the US Dollar but trimmed their positioning to $12.4 billion in the week ending May 20 from $16.5 billion in the week prior, according to CFTC data reported Friday, Reuters reports.
- Trump announced he would extend to July 9 the deadline for the European Union (EU) to face 50% tariffs. The decision came after a call between Trump and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen on Sunday, and should help the EU negotiate a trade deal with the Trump administration, Bloomberg reports.
- The US economic calendar is almost empty on Monday due to the Memorial Day public holiday in the US. Later this week, the second reading for the US Gross Domestic Product of the first quarter is due on Thursday. The Personal Consumption Expenditure data for April is due Friday.
- Equities are rallying in the brief sigh of relief on the US tariffs delay. European equities are surging over 1%, together with US futures.
- The CME FedWatch tool shows the chances of an interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve in June’s meeting are only at a low 5.6%. Further ahead, the July 30 meeting sees odds for rates being lower than current levels at 23.9%.
- The US 10-year yields will not move this Monday as US markets remain closed due to the Memorial Day public holiday.
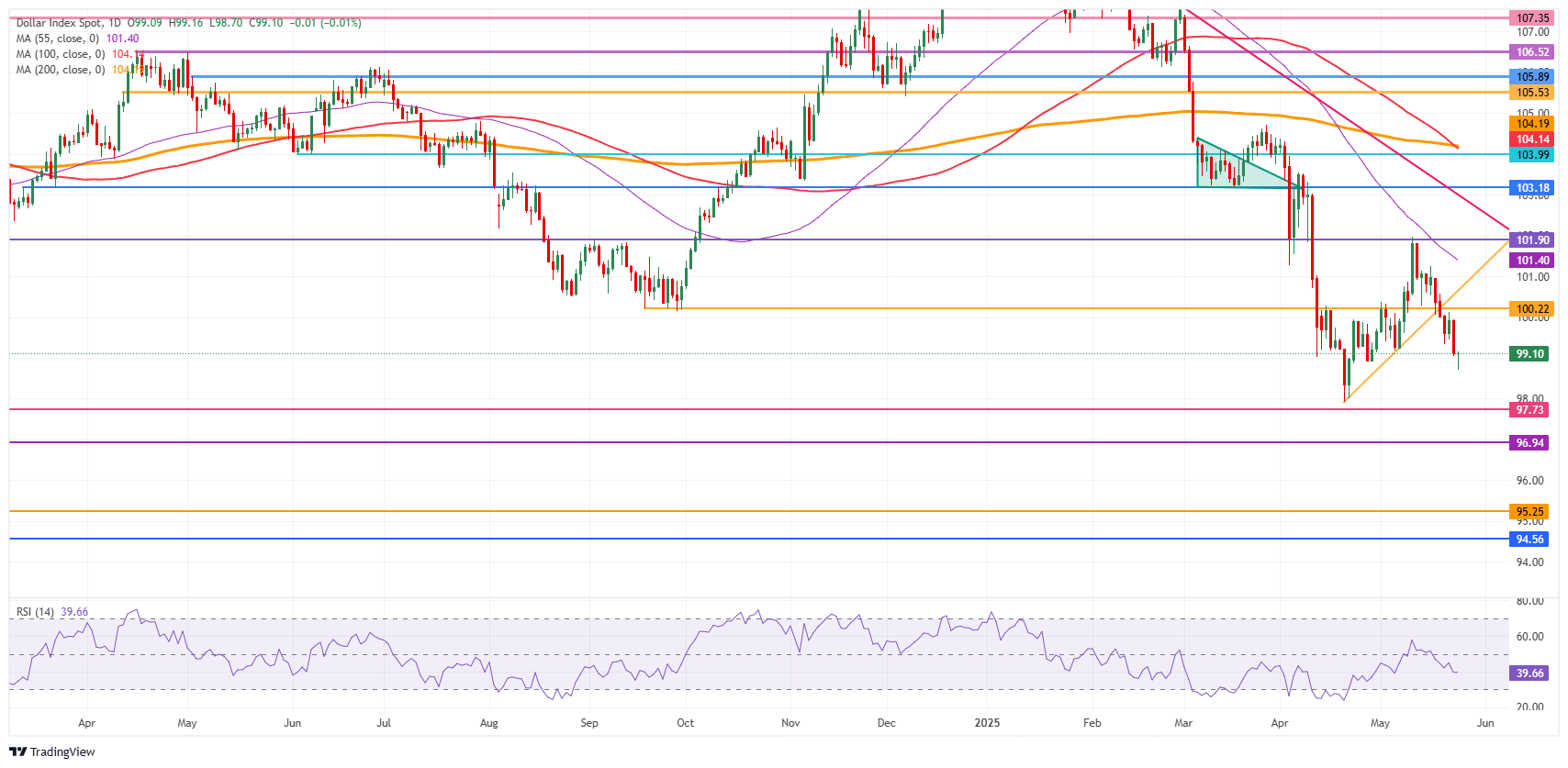
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Never a straight line
The US Dollar Index recovers from daily lows on Monday, with some adventurous bulls coming in to buy the dip, which materialized in early Asian trading. With the Relative Strength Index (RSI) starting to break below 40 and nearing the oversold barrier, some slowdown and even a turnaround in the DXY could take place. The recovery could be short-lived, though, as several macroeconomic issues are still unresolved.
On the upside, the 100.22 level, which held the DXY back in September-October, is the first resistance, followed by the broken ascending trend line near 100.80 on Monday. Further up, the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 101.39 is the next level to watch out for, followed by 101.90, a pivotal level throughout December 2023 and a base for the inverted Head-and-Shoulders (H&S) formation during the summer of 2024. In case US Dollar bulls push the DXY even higher, the 103.18 pivotal level will come into play.
If the downward pressure continues, a nosedive move could materialize towards the year-to-date low of 97.91 and the pivotal level of 97.73. Further below, a relatively thin technical support comes in at 96.94 before looking at the lower levels of this new price range. These would be at 95.25 and 94.56, meaning fresh lows not seen since 2022.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.

